Agentless Overview
General Information
The Cloudamize Agentless Data Collector can be used to discover and assess physical and virtual machines without installing software agents on each machine throughout your infrastructure.
The collector is deployed on a physical Windows server or Windows virtual machine and can be used to discover and assess both Windows and Linux machines. Each collector can be used to monitor up to 500 machines. Additional collectors can be installed on additional machines to monitor larger infrastructures.
Example:
1-500 machines = 1 collector
501-1000 machines = 2 collectors
1001-1500 machines = 3 collectors
The Cloudamize Agentless Data Collector uses SSH to discover and communicate with Linux machines on the subnet, and WMI/RPC to discover and communicate with Windows machines. The collector then sends the TLS v1.3 encrypted data to the Cloudamize servers for processing.
MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) is not supported for connections to Windows or Linux nodes from the Agentless Data Collector.
Agent-Based VS Agentless
There are advantages and disadvantages to utilizing the Cloudamize Agentless Data Collector as opposed to installing software agents throughout the infrastructure. One obvious advantage will be in the case of high-security compliant infrastructures, which are not permitted to install software and communicate out to remote servers from each machine in the infrastructure. The Cloudamize Agentless Data Collector can be installed on one machine in cases like this, and the entire infrastructure being assessed will send that data to this one machine over WMI (Windows) and SSH (Linux). All of this communication happens on the internal network, and data will only leave the network from the machine with the collector installed.
The table below highlights the feature comparison between agent-based and agentless data collection.
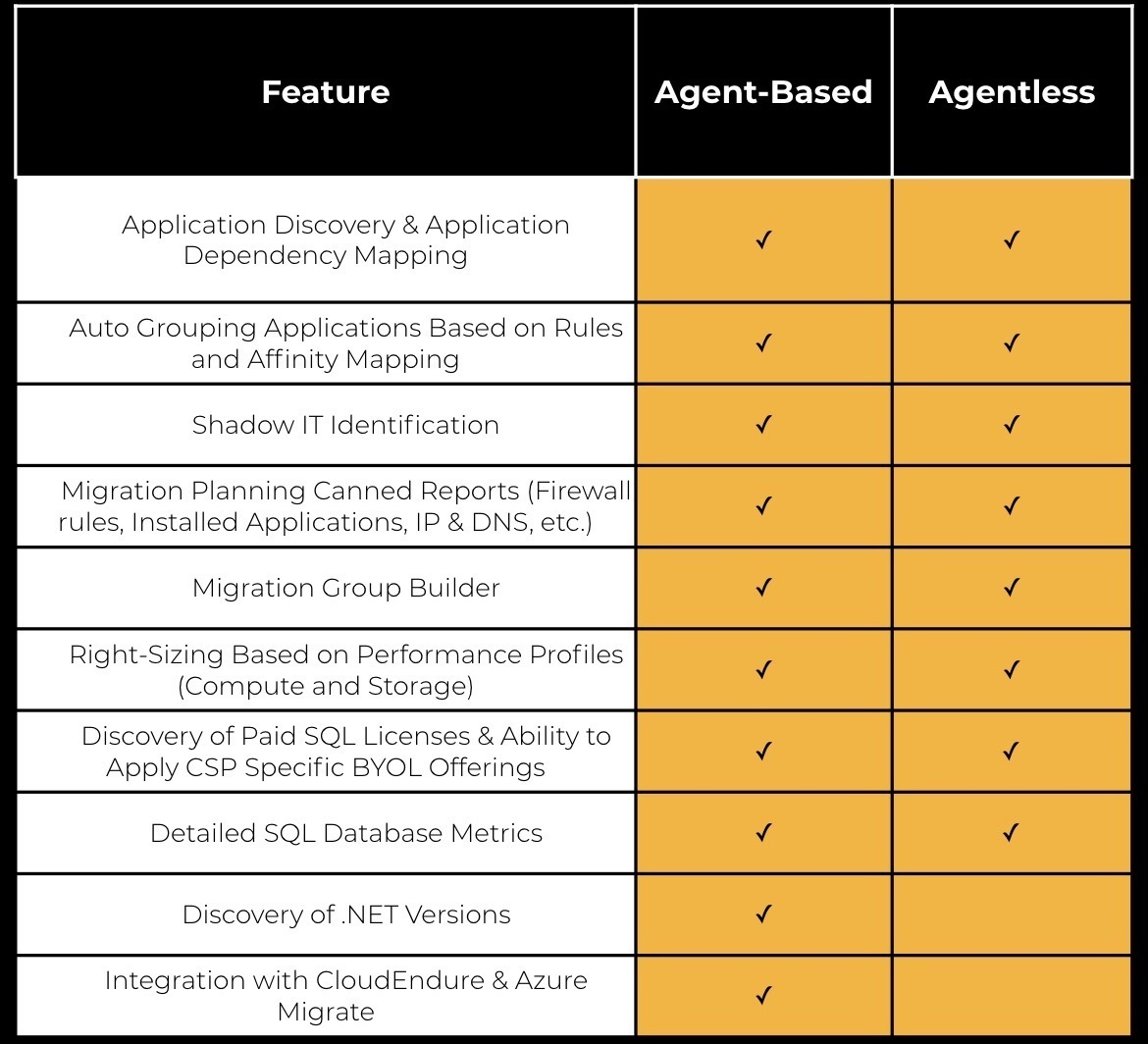
Note: The details on the Basic and Advanced SQL Data collected are available here.
Disadvantages of agentless
Without having software agents installed on each machine, there are also disadvantages in a few areas. The following table shows a set of metrics and the impact that taking an agentless approach will have.
Metric | Impact |
Short-lived connections | If a connection is short-lived, it is not captured, and that may result in missed inter-connectivity |
Lower performance resolutions | The monitoring window is every 5 minutes rather than every 30 seconds. Possible to miss short-term peaks |
Performance Throttling | Agentless monitoring does not have a performance controlling mechanism on the monitored host |
Supported MS SQL data collected by Agent-Based and Agentless
Data | Agent | Agentless |
|---|---|---|
MS SQL Server instance id (e.g. MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER) | ✔ | ✔ |
MS SQL Server instance name (e.g. MSSQLSERVER) | ✔ | ✔ |
Server edition (e.g. Standard Edition) | ✔ | ✔ |
Server edition type (e.g. Standard Edition) | ✔ | ✔ |
Server version (e.g. 9.4.5000.00) | ✔ | ✔ |
Server patch level | ✔ | ✔ |
Server service pack (e.g. 4) | ✔ | ✔ |
SQL Server binary directory with full path (e.g. C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Binn) | ✔ | ✔ |
Information for each database (e.g. "database name (e.g. LicensingService), database total size in MB (e.g. 40)) | ✔ | ✔ |
Database file location (e.g. C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\LicensingService.mdf) | ✔ | ✔ |
Active or passive in clustered SQL servers | ✔ | ✔ |
SQL Server data path (e.g., C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA) | ✔ | ✔ |
Error log file with full path, e.g., C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log\ERRORLOG) | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Linked Servers | ✔ | ✔ |
Cluster name | ✔ | ✔ |
Cluster state | ✔ | ✔ |
Feature list | ✔ | ✔ |
SQL Server product information | ✔ | ✔ |
SQL Server license info | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Version | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Version Number | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Edition | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL in a Failover Cluster is clustered | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL is HA-DR | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Cluster Name | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Quorum Type | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance Is the SQL Availability Group Primary | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group Primary | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group Replicas | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group Role | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance Is a SQL Availability Group Readable Secondary | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group Using Synchronous Replication | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Availability Group Failover Mode | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL FileStream Status | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL PolyBase Status | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL FullText Status | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL PerfMonMode | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance Lic SQL By | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Collation | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Max Server Mem in MB | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL XP Cmd Shell Status | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL CLR Status | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL DB Count | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL DB Encryption Present | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL DB Mirroring Present | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL DB Replication Present | ✔ | ✔ |
Instance SQL Total DB Size MB | ✔ | ✔ |
